- 1. Basics
- How to Compare Arrays in PostgreSQL
- How to Concatenate Strings in PostgreSQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Create an Array
- How to Insert Array Data Into a Table
- How to Insert Data Into an Array
- How to Modify Arrays
- How to Query Arrays
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- How to Convert Local Time to UTC
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Use generate_series to Avoid Gaps In Data
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MS-SQL Server
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Create an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Drop an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Create a View in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a View in MS-SQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MS-SQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MS-SQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Extract a Component From a Datetime
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MS-SQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MySQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to use group_concat()
- How to do you Use a substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MySQL
- How to Drop a Table in MySQL
- How to Rename a Table in MySQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MySQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MySQL
- How to Add a Column in MySQL
- How to Drop a Column in MySQL
- How to Rename a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MySQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Create an Index in MySQL
- How to Drop an Index in MySQL
- How to Create a View in MySQL
- How to Drop a View in MySQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MySQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MySQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MySQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in Oracle
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use listagg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in BigQuery
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to use substring() function
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Database in BigQuery
- How to Create a Table in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Table in BigQuery
- How to Rename a Table in BigQuery
- How to Truncate Table in BigQuery
- How to Duplicate a Table in BigQuery
- How to Add a Column in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Create a View in BigQuery
- How to Drop a View in BigQuery
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
Visual Representation of SQL JOINS
- 1. Basics
- How to Compare Arrays in PostgreSQL
- How to Concatenate Strings in PostgreSQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Create an Array
- How to Insert Array Data Into a Table
- How to Insert Data Into an Array
- How to Modify Arrays
- How to Query Arrays
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- How to Convert Local Time to UTC
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Use generate_series to Avoid Gaps In Data
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MS-SQL Server
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Rename a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MS-SQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MS-SQL
- How to Create an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Drop an Index in MS-SQL
- How to Create a View in MS-SQL
- How to Drop a View in MS-SQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MS-SQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MS-SQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Extract a Component From a Datetime
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use Lateral Joins
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MS-SQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in MySQL
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to use group_concat()
- How to do you Use a substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table in MySQL
- How to Drop a Table in MySQL
- How to Rename a Table in MySQL
- How to Truncate a Table in MySQL
- How to Duplicate a Table in MySQL
- How to Add a Column in MySQL
- How to Drop a Column in MySQL
- How to Rename a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in MySQL
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column in MySQL
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in MySQL
- How to Create an Index in MySQL
- How to Drop an Index in MySQL
- How to Create a View in MySQL
- How to Drop a View in MySQL
- How to Alter Sequence in MySQL
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time in MySQL
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting in MySQL
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in Oracle
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to Replace Substrings
- How to Trim Strings
- How to Use listagg()
- How to Use substring()
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Insert
- How to Update
- How to Delete
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Table
- How to Drop a Table
- How to Rename a Table
- How to Truncate a Table
- How to Duplicate a Table
- How to Add a Column
- How to Drop a Column
- How to Rename a Column
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column
- How to Remove a Default Value From a Column
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint
- How to Create an Index
- How to Drop an Index
- How to Create a View
- How to Drop a View
- How to Alter Sequence
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Import a CSV
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Query a JSON Column
- How to Use Filter Clause to Have Multiple Counts
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
- 1. Basics
- How to Concatenate Strings in BigQuery
- How to Convert the Case of a String
- How to replace a Substring in a String
- How to Trim a String
- How to Use string_agg()
- How to use substring() function
- How to Use substring() with Regular Expressions
- How to Use BETWEEN Correctly
- How to use insert into statement
- How to use Update statement in SQL
- How to use Delete SQL Statement
- 2. Database Management
- How to Create a Database in BigQuery
- How to Create a Table in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Table in BigQuery
- How to Rename a Table in BigQuery
- How to Truncate Table in BigQuery
- How to Duplicate a Table in BigQuery
- How to Add a Column in BigQuery
- How to Drop a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Default Value to a Column in BigQuery
- How to Add a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Remove a Not Null Constraint in BigQuery
- How to Create a View in BigQuery
- How to Drop a View in BigQuery
- 3. Dates And Time
- How to Exclude Current or Partial Weeks
- How to Query Date and Time
- How to Group by Time
- How to Round Timestamps
- 4. Analysis
- How to Use nullif()
- How to Get the First Row per Group
- How to Do Type Casting
- How to Write a Common Table Expression
- How to Compare Two Values When One Is Null
- How to Use Coalesce
- How to Write a Case Statement
- How to Calculate Cumulative Sum-Running Total
The examples in this lesson show several SQL JOIN operations and Venn diagrams to show the result sets of records expected for each JOIN type. A non-equality JOIN expression is also shown.
Sample Tables
There are two sample tables, man and woman, with three attributes each: first_name, last_name and marriage_id. You can JOIN both tables using the marriage_id column.
Table Woman
| First_name | Last_name | Marriage_id |
|---|---|---|
| Mary | Lee | 100 |
| Susan | Graue | NULL |
| Meiling | Yung | NULL |
| Dipali | Gupta | 101 |
Table Man
| First_name | Last_name | Marriage_id |
|---|---|---|
| Simon | Ming | NULL |
| Peter | Duck | 101 |
| Juan | Perez | 100 |
| Dmitry | Shepev | NULL |
In the SQL JOINS lesson you learned the JOIN clause needs a shared column appearing in both tables to combine them. In the sample tables the column is marriage_id.
Here is a representation of the tables in Venn diagrams:
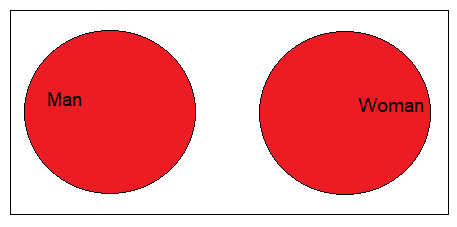
Here is a query to obtain the men and women who are married:
SELECT
M.first_name AS man_first_name,
M.last_name AS man_last_name,
W.first_name AS woman_first_name,
W.last_name AS woman_last_name
FROM Man M INNER JOIN Woman W ON M.marriage_id = W.marriage_id
Here are the results using a Venn diagram:
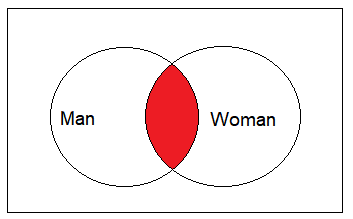
Here are the resulting records:
| man_first_name | man_last_name | woman_first_name | woman_last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peter | Duck | Dipali | Gupta |
| Juan | Perez | Mary | Lee |
For the second SQL JOIN example, suppose you want to obtain the names of all women, married or not. In addition, for women who are married you want the name of the men.
Here is the Venn representation of the expected result:
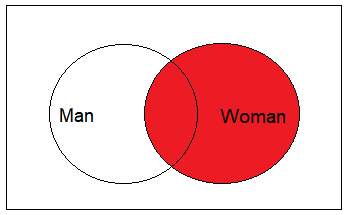
Here is the query to obtain the results:
SELECT
W.first_name AS woman_first_name,
W.last_name AS woman_last_name,
M.first_name AS man_first_name,
M.last_name AS man_last_name
FROM Woman W LEFT JOIN Man M ON W.marriage_id = M.marriage_id
The query to obtain all women is a LEFT JOIN. You know from the SQL JOINS lesson that LEFT JOIN returns all records from the left side table regardless if they have a match in the right side table.
Here are the resulting records, with NULL set by LEFT JOIN where there is not a match:
| woman_first_name | woman_last_name | man_first_name | man_last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dipali | Gupta | Peter | Duck |
| Mary | Lee | Juan | Perez |
| Susan | Graue | NULL | NULL |
| Meiling | Yung | NULL | NULL |
You can leverage the NULL assigned to records from the Man table and create a query to obtain Women who are not married.
Here is the Venn representation of the expected result:
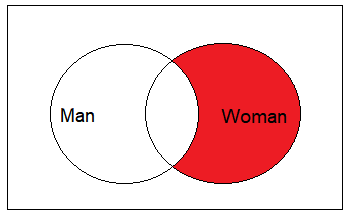
Here is the query:
SELECT
W.first_name AS woman_first_name,
W.last_name AS woman_last_name,
M.first_name AS man_first_name,
M.last_name AS man_last_name
FROM Woman W LEFT JOIN Man M ON W.marriage_id = M.marriage_id
WHERE M.marriage_id IS NULL
Here are the resulting records
| woman_first_name | woman_last_name | man_first_name | man_last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Susan | Graue | NULL | NULL |
| Meiling | Yung | NULL | NULL |
SQL FULL JOIN Operator
The SQL FULL JOIN operator returns all matching records from both tables whether the other table matches or not. FULL JOIN and FULL OUTER JOIN are the same.
Suppose you want to obtain the all women and men who are not married, as represented in the Venn diagram:
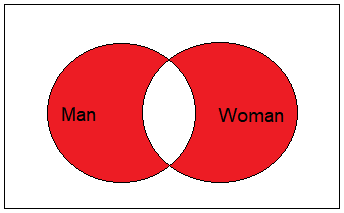
Here is the query:
SELECT
W.first_name AS woman_first_name,
W.last_name AS woman_last_name,
M.first_name AS man_first_name,
M.last_name AS man_last_name
FROM Woman W FULL JOIN Man M ON W.marriage_id = M.marriage_id
WHERE M.marriage_id IS NULL OR W.marriage_id IS NULL
Using the SQL FULL JOIN operator obtains the records from both tables. NULL is assigned where there is not a matching record:
| woman_first_name | woman_last_name | man_first_name | man_last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| NULL | NULL | Dmitry | Shepev |
| NULL | NULL | Simon | Ming |
| Susan | Graue | NULL | NULL |
| Meiling | Yung | NULL | NULL |
Obtaining All The Records from Both Tables
In this example, you want to obtain all of the records:
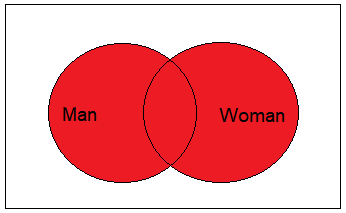
You can reuse the previous query, without the IS NULL comparison for marriage_id:
SELECT
W.first_name AS woman_first_name,
W.last_name AS woman_last_name,
M.first_name AS man_first_name,
M.last_name AS man_last_name
FROM Woman W FULL JOIN Man M ON W.marriage_id = M.marriage_id
Here is the result:
| woman_first_name | woman_last_name | man_first_name | man_last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| NULL | NULL | Dmitry | Shepev |
| NULL | NULL | Simon | Ming |
| Susan | Graue | NULL | NULL |
| Meiling | Yung | NULL | NULL |
| Dipali | Gupta | Peter | Duck |
| Mary | Lee | Juan | Perez |
There are some cases not covered in this lesson. Most of these cases are symmetric with other covered cases. For example, there was not as example for unmarried men:
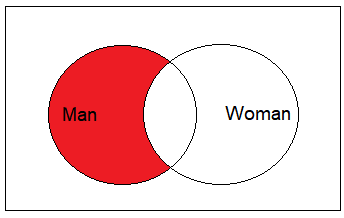
The unmarried women example is the mirror image case:
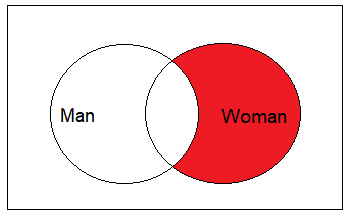
SQL JOIN Using Non-Equality Expressions
Here is a final JOIN example using non-equality expressions.
Suppose you run a shop and your database has a product table with the columns: product_id, name, price and stock.
| product_id | name | price | stock |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | headphones H1 | $30 | 120 |
| 101 | headphones F2 | $25 | 80 |
| 102 | Cell phone M23 | $210 | 130 |
| 103 | Cell phone A22 | $219 | 320 |
| 104 | Cell phone A25 | $270 | 120 |
| 105 | wireless headphones H2 | $80 | 250 |
| 106 | wireless headphones H3 | $135 | 120 |
For the holidays, you want to create a special offer with a bundle of two products, but you need more data to decide which products to include. You want a query to obtain all the possible candidate pairs of products for the bundle meeting your criteria:
- Products in stock with more than 100 units
- Combined price of both products in the range $200 to $350
Here is the query to obtain all the possible product pairs:
SELECT
P1.name AS name_product1,
P2.name AS name_product2,
P1.price + P2.price AS bundle_price,
P1.stock AS stock_product1,
P2.stock AS stock_product2
FROM Product P1 INNER JOIN Product P2 ON P1.product_id > P2.product_id
WHERE P1.stock > 100
AND P2.stock > 100
AND P1.price + P2.price BETWEEN 200.0 AND 350.0
ORDER BY P1.name, P2.name ;
Here are the results:
| Name Product1 | Name Product2 | Bundle_Price | Stock Product1 | Stock Product2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell phone A22 | headphones H1 | 249 | 320 | 120 |
| Cell phone A25 | headphones H1 | 300 | 120 | 120 |
| Cell phone M23 | headphones H1 | 240 | 130 | 120 |
| wireless headphones H2 | Cell phone A22 | 299 | 250 | 320 |
| wireless headphones H2 | Cell phone A25 | 350 | 250 | 120 |
| wireless headphones H2 | Cell phone M23 | 290 | 250 | 130 |
| wireless headphones H3 | Cell phone M23 | 345 | 120 | 130 |
| wireless headphones H3 | wireless headphones H2 | 215 | 120 | 250 |
If you do not use the condition P1.product_id > P2.product_id you have even more candidate pairs, including pairs with the same product on both sides and duplicated pairs like <Product1, Product2 > and <Product2, Product1> .
Closing Words
This lesson presented visual representations to illustrate the resulting datasets of the JOIN operator. You also learned an interesting query using a JOIN with a non equality condition. Keep going, learn SQL and increase your skills!
IN THIS PAGE





